How Oxygen Levels Influence Sleep Apnea
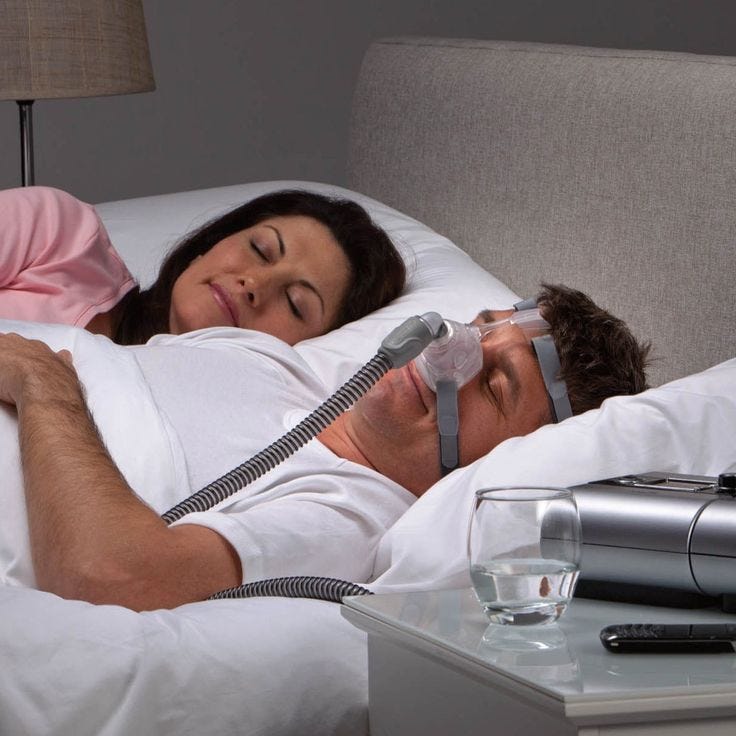
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy increases oxygen levels, adding an average of 33 minutes to sleep duration.
People with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) often have blood oxygen levels below 95% while sleeping, increasing the risk of Hypoxemia, where tissues lack the oxygen needed for proper function. This can lead to fatigue, dizziness, and headaches the next day. Over time, OSA-related oxygen deficiency can raise the risk of stroke, brain aneurysms, and cognitive decline. Research by Tachikawa et al. (2017), published in the National Library of Medicine, shows that Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy increases oxygen levels, adding an average of 33 minutes to sleep duration.
In this article, NOTT explores the impact of oxygen on sleep and overall health, offering recommended solutions for Sleep Apnea to enhance quality of life.
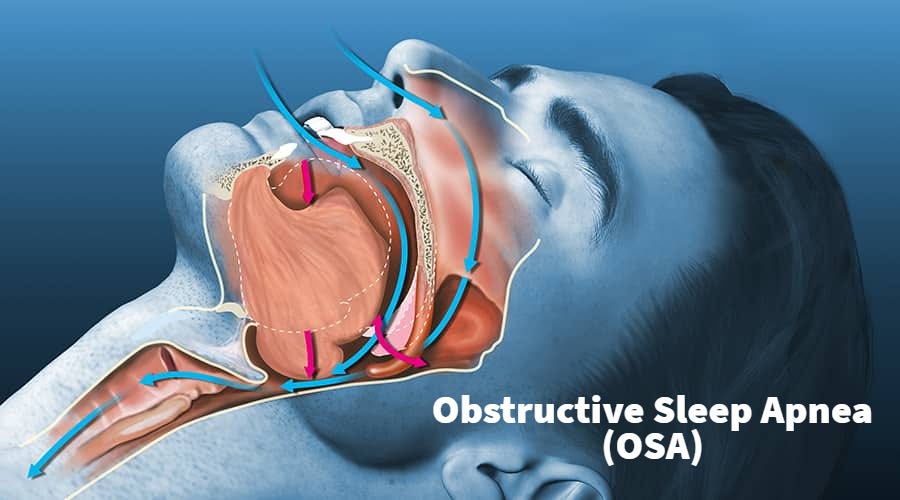
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is the periodic reduction (hypopnea) or cessation (apnea) of airflow due to the narrowing of the upper airway during sleep, often accompanied by hypoxemia and sleep disturbance. The prevalence of OSA is estimated to be between 2% and 25% in the general population.OSA is linked to hypertension, ischemic heart disease, stroke, premature death, and motor vehicle crash.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea due to the narrowing of the upper airway during sleep
Sleep Apnea and Normal Blood Oxygen Levels
Blood oxygen levels—also known as oxygen saturation levels—typically range from 95% to 100% in healthy individuals, whether awake or asleep. However, when oxygen saturation levels drop below normal, you may experience Breathlessness, Insomnia, or Sleep Apnea.
The interpretation of oxygen saturation levels
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Sleep Apnea is a dangerous condition if not detected and treated in time. Below are some signs of Sleep Apnea:
Loud snoring
Stopped breathing or choking during the night
Gasping for air during sleep
Awakening with a dry mouth
Morning headache
Difficulty staying asleep, known as Insomnia
Excessive daytime sleepiness, known as Hypersomnia
Irritability and feeling on edge
Feeling tired or drowsy during the day, or falling asleep while driving, reading, or working
Difficulty concentrating or remembering things
Frequent nighttime urination
Other symptoms: Depression, anxiety, erectile dysfunction, reduced sex drive, and heartburn at night
To identify the patients at risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), the STOP-BANG questionnaire is an easily administrable tool with high sensitivity. Patients with a score of 0 to 2 have a low risk of OSA whereas those with a score of 5 to 8 have a high risk of moderate – severe OSA (AHI >15). This screening tool enables you to perform a quick self-assessment at home. However, we recommend visiting a nearby medical facility for further evaluation if you notice any unusual symptoms.
The Role of Oxygen in Sleep Apnea
1. What is Supplemental Oxygen?
Supplemental Oxygen therapy involves providing natural or using oxygen machines to maintain blood oxygen saturation levels and support breathing for individuals experiencing respiratory difficulties. Oxygen (O2) has been used as an effective treatment for patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) who are non-compliant with Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy, helping to mitigate the harmful effects of intermittent oxygen deprivation during sleep. Supplemental oxygen has been proven effective in improving respiration, reducing nighttime apnea episodes, and alleviating snoring.
2. How Oxygen Helps with Sleep Apnea
Oxygen enrichment has been shown to significantly reduce Sleep Apnea and improve breathing patterns, particularly at high altitudes. According to Luks AM et all (1998) research, Eighteen sea-level residents slept one night in ambient air, and another night in 24% oxygen. Participants sleeping in oxygen-enriched air experienced fewer apneas and reduced time spent in periodic breathing compared to ambient air.
These improvements were accompanied by enhanced sleep quality, lower acute, and increased arterial oxygen saturation, indicating better oxygen delivery to the body overnight. By altering the control of breathing, supplemental oxygen can alleviate the disruptions caused by apnea, offering a practical and effective solution to enhance sleep and overall well-being.
Oxygen therapy is also recommended for Sleep Apnea patients in specific situations. This includes cases where patients continue to experience significant oxygen desaturation despite using Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy or for those with comorbid conditions affecting oxygen levels, such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). The decision to use oxygen therapy should always be made under the guidance of a sleep specialist, who can assess the individual’s specific needs and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
3. Oxygen Therapy Options for Sleep Apnea
When it comes to oxygen therapy for Sleep Apnea, several options are available. One of the most common approaches is the use of oxygen machines for sleep: revolutionizing the treatment of Sleep Apnea. These devices, including CPAP machines with supplemental oxygen, can provide more comprehensive treatment for individuals with complex Sleep Apnea or those who do not respond adequately to CPAP therapy.
The patient uses a CPAP machine to help with Sleep Apnea and improve breathing
Another option is Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy, which involves delivering oxygen directly through small tubes placed in the nostrils. This method can be used independently or in combination with CPAP therapy. However, both therapies can cause discomfort during sleep due to the need to wear devices on the face.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Chambers are modern medical devices that deliver pure oxygen at pressures higher than normal, supporting improved health and physical recovery. This method helps enhance metabolism, heal wounds, rejuvenate skin, boost the immune system, and reduce fatigue. Not only used by patients, but many athletes also utilize this therapy for recovery after training. Additionally, it promotes relaxation, improves sleep quality, and enhances overall health. However, the high cost makes it less suitable for regular use.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Chambers provide pure oxygen to the patients
Pioneering in the field of Sleep Healthcare to optimize user comfort during sleep, NOTT has launched the SmartBed—an ecosystem for the perfect sleep experience. Unlike other SmartBeds on the market, the NOTT SmartBed is equipped with an advanced oxygen system integrated into a comfortable bed. You only sleep like a baby—the sensors measure the oxygen levels in your bedroom and your body. Based on this data, the AI algorithm adjusts the necessary oxygen levels during sleeping time.
Additionally, the SmartBed uses the 525DS oxygen filter membrane, which removes bacteria, dust, PM, pollutants, smoke, pollen, and pet dander in the bedroom. The NOTT SmartBed provides 99.8% fresh oxygen flow to the body, helping to decrease sleep apnea, snoring, and breathlessness autonomously, and allowing you to start your day with a smile.
The NOTT SmartBed delivers fresh oxygen to enhance the sleep experience
Conclusion
Oxygen therapy has proven to be an effective solution for enhancing sleep quality and reducing the risks associated with Sleep Apnea. To elevate both the quality of sleep and overall health, the NOTT SmartBed—a new era in sleep healthcare with its advanced capabilities can be integrated with other information to screen for Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) risks. AI-powered oxygen technology and a supportive frame ensure personalized care and optimal alignment for those with Sleep Apnea. Embrace the future of sleep healthcare with NOTT SmartBed to get better sleep, improved health, and more restful night.